Algorithms
- Algorithms
- Application
- New Application
- Actions
- Snippets
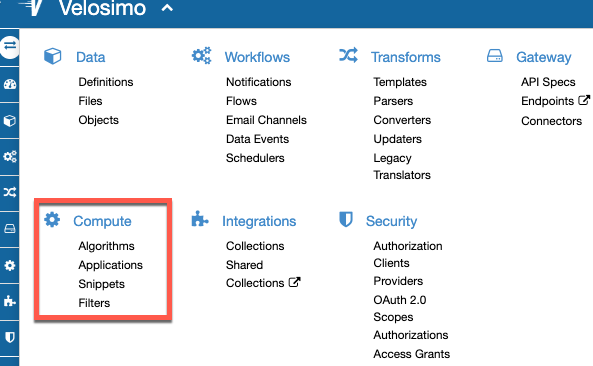
Compute
The Compute menu is where the user can define the algorithms, applications and review the snippets. Essentially, all regarding with code.
Algorithms
Algorithms are pieces of logic that you can choose to execute and chain in order to process data. They will be found into Compute/Algorithm Menu.
Algorithm's attributes
Algorithm's Name
Algorithm names must be valid method names and this must start with a letter and not contain white spaces or any special characters.
Algorithm's Parameter
Algorithms can have many parameters, each with their own individual fields.
The name of parameters besides the logical function of allowing you to recognize it on the administration interface, is also used as the name of the variable holding its value in the Algorithm’s code, so it must be a valid variable name.
In case of the algorithm be the type:
- before_submit: should have as required parameters the variables "options" and "task" in this order.
- after_calback: should have as required parameter the variable "task".
Parameter's type
You can leave a parameter untyped, which means it will accept any value passed on to it, or you can set a type for it in order to easily validate that the code receives what it expects.
Currently available types include:
- integer for integer numbers.
- number for floating point precision numbers.
- boolean for boolean true or false values.
- string for strings of characters.
- hash for dictionary-like objects holding a set of key: value pairs. Best to represent complex objects.
Parameter's Many attr
If checked the parameter will be treated as an array rather than a singular object.
Parameter's Required attr
If unchecked a default value must be provided.
Parameter's Default attr
Only available if the parameter is not required, this value will be used when no value is specified on execution.
It is important to note that all required parameters must be declared before the optional ones.
Algorithm's Code
The actual code of the algorithm, must be written in Ruby, parameters can be accessed by their names.
The code of an algorithm is located into snippets.
Algorithm's Store Output
If checked Velosimo will attempt to store the output of the algorithm on a DataType record (or records if the output is an array).
-
Output DataType
Only available if Store Output is checked. If left blank a new FileDataType will be created. When storing output on file data type records, the mime type of the file will be guessed from the output.
-
Validate Output
Only available if an Output DataType is selected for the output storage. This will prevent chaining further algorithm executions in the output cannot be validated against the chosen data type, otherwise, it will fail silently and allow any chaining to carry on.
Algorithm Execution ways
An algorithm can be executed in these ways:
- Run Algorithm option.
- Task algorithm scheduled.
- Via code.
- Before_submit field of a flow.
- After_callback of a flow.
- As an application action.
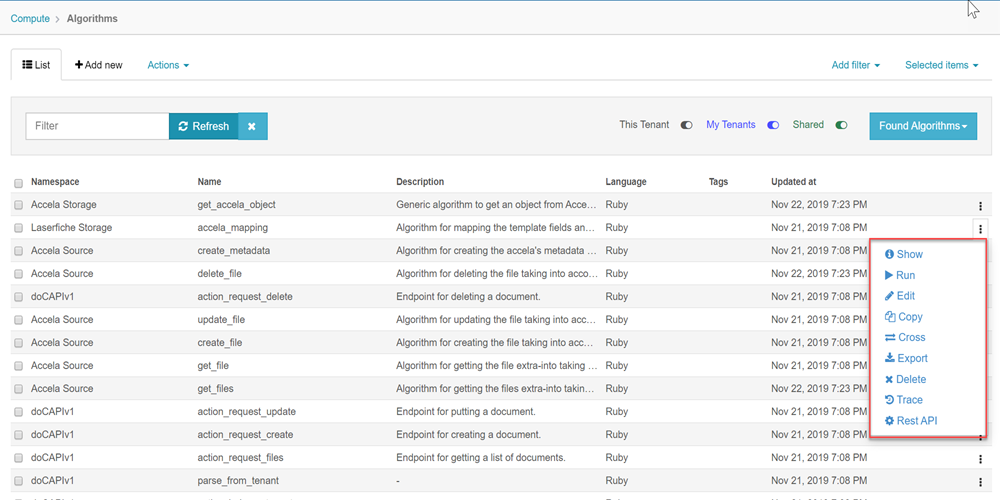
Run Algorithm
You can execute an algorithm by a run option.
Then you should enter the parameters for the execution, and if you want run as background.
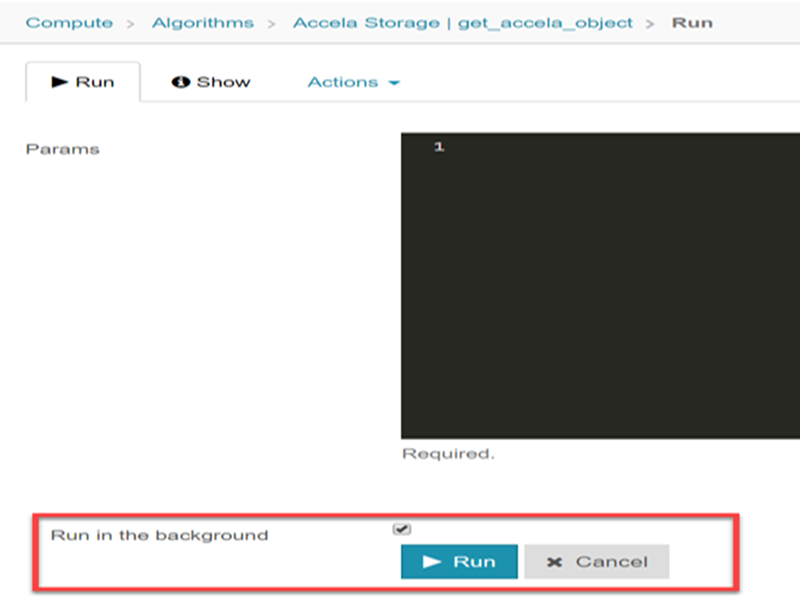
Run as background implies that the execution will trigger as background in a tasks queue.
Task Algorithm Scheduled
When you ran the algorithm, you can associate the task to a scheduler created.
Select the task triggered by the algorithm execution.
Associate the task to the scheduler.
 To see more about a scheduling visit Workflow > Schedulers
To see more about a scheduling visit Workflow > Schedulers
Sometimes you will need execute algorithms inside another algorithms or translators.
The way to call an algorithm inside a code is:
Cenit.namespace('Accela').algorithm('get_record').run()
If the alrotihm has parameters, execute it with this way:
Cenit.namespace('Accela').algorithm('get_record').run([parameters])
- parameters: hash of algorithm parameters.
If you call an algorithm inside a translator or algorithm with the same namespace, you only can call it with the name: get_record() or get_record([parameters])
Before_submit field of a Flow
This algorithm that you want to be executed before the translator of the flow is executed. It’s listed in the algorithms list. This algorithm must have the parameters: options and task, in this order.
After_callback of a Flow
Algorithms executed after flow processing, execution state is supplied as argument with the "task" parameter.
To see more information on Flows visit Workflow > Flows
Application's Action
This is the algorithm that the application will execute when its path is consulted. What this algorithm returned will be rendered to the application URL path. This algorithm must have as parameters: control and params.
To see more information on Applications visit Compute > Application
Algorithm Notifications
Inside the algorithm code, you can write some notification points, like this:
Tenant.notify(message: "Something")
